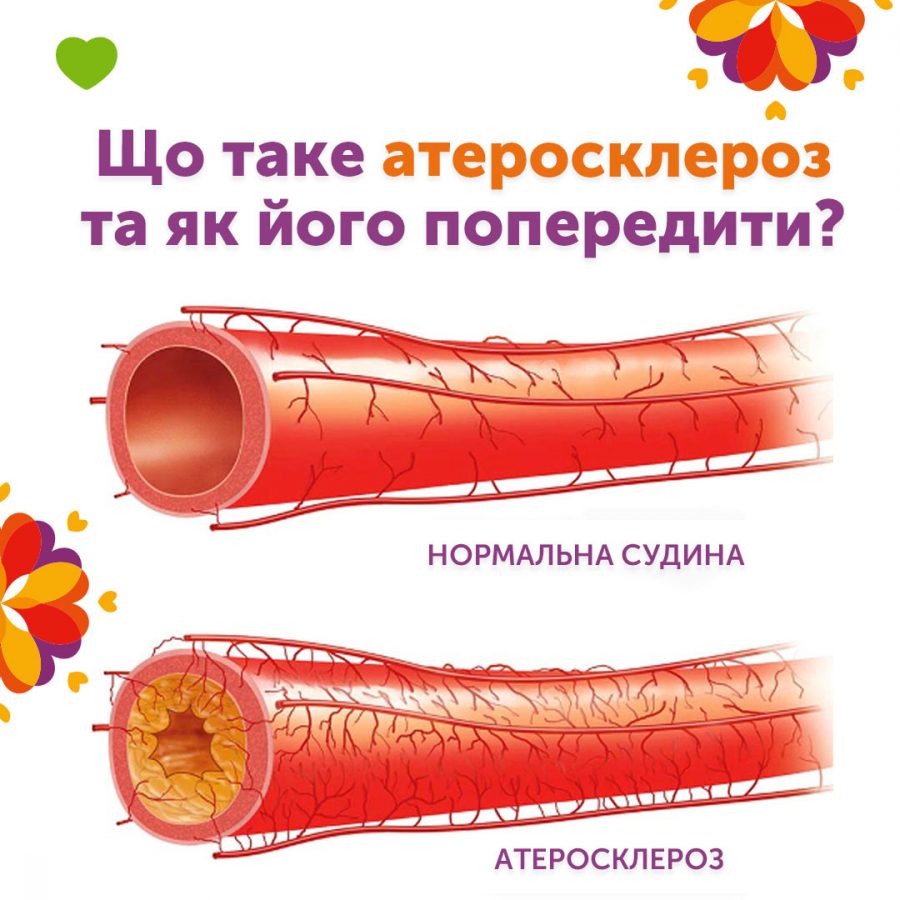
Atherosclerosis is a disease in which fatty deposits, primarily cholesterol, accumulate in the
walls of arteries, leading to narrowing or even complete blockage of the arteries. This can
result in serious health issues such as heart attack, stroke, and peripheral arterial disease. Atherosclerosis is responsible for 85% of all deaths due to cardiovascular diseases.
Why is atherosclerosis dangerous and often leads to serious complications?
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is often invisible, as many people do not experience
any symptoms until complications arise. Fatty deposits, or plaque, can detach within the
arteries, causing a clot to form, which blocks the artery. This can disrupt blood flow and lead
to a heart attack or stroke.
Atherosclerosis is particularly dangerous for older people, those with a family history of
cardiovascular diseases, smokers, individuals with high blood pressure, diabetics, people with
a sedentary lifestyle, and those who are overweight. Stress, especially chronic stress, is also
an important risk factor for the development of atherosclerosis.
How can we detect if we have atherosclerosis?
An ultrasound examination of the carotid arteries can reveal the condition and patency of the
arteries, as well as the presence of atherosclerotic plaques. The examination is safe, non-
invasive, painless, and has no contraindications.
Regular cholesterol monitoring is also important. A full lipid profile shows the levels of
"good" (HDL) and "bad" (LDL) cholesterol, triglycerides. LDL cholesterol is a key factor in
the development of atherosclerosis, so it is important to regularly monitor and maintain it at
recommended levels. Consistent and long-term lowering of LDL cholesterol levels can halt
the progression of atherosclerosis and prevent cardiovascular events such as heart attacks,
strokes, or peripheral arterial disease.
How can we prevent the development of atherosclerosis?
If we are aware of the risk factors that we can control, we can significantly reduce the risk of
developing atherosclerosis. Preventing atherosclerosis involves several aspects of a healthy
lifestyle:
Healthy diet (less saturated fat, more vegetables, less salt, sugar, etc.),
Regular physical activity and weight management,
Monitoring blood pressure and blood sugar,
Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption,
Stress management,
Regular intake of prescribed medications and following your doctor’s advice.
By properly controlling cholesterol, undergoing regular ultrasound screenings, and adopting
preventive measures, it is possible to significantly reduce the risk of developing
atherosclerosis and greatly improve overall health.
Addiction information:
Leave your email
and we will contact you soon